Introduction to Precipitation
Imagine stepping outside and feeling the soft touch of snowflakes dancing around you. Or picture a warm summer day interrupted by an unexpected downpour. Precipitation is nature's way of keeping our world vibrant and alive, offering endless surprises in its various forms. From gentle drizzles to heavy snowstorms, precipitation plays a crucial role in shaping our climate and ecosystems. But how much do we really know about this fascinating phenomenon? Let’s embark on a journey through the diverse types of precipitation, uncovering the secrets behind each drop and flake that falls from the sky.
Types of Precipitation
Precipitation comes in various forms, each with its unique characteristics. Rain is the most common type, falling as liquid droplets when temperatures are above freezing. It nourishes plants and replenishes water sources.
Snow is another captivating form of precipitation. It occurs when temperatures dip below freezing, allowing water vapor to crystallize into delicate snowflakes. Each flake has a distinct pattern, making winter landscapes truly magical.
Sleet forms when raindrops freeze before reaching the ground, resulting in small ice pellets that can create slippery surfaces. Then there’s hail, which develops during strong thunderstorms with powerful updrafts ice balls that can cause significant damage.
Drizzle offers a light misty rain that often accompanies cloudy days. These varied types highlight nature's creativity and play an essential role in our ecosystems.
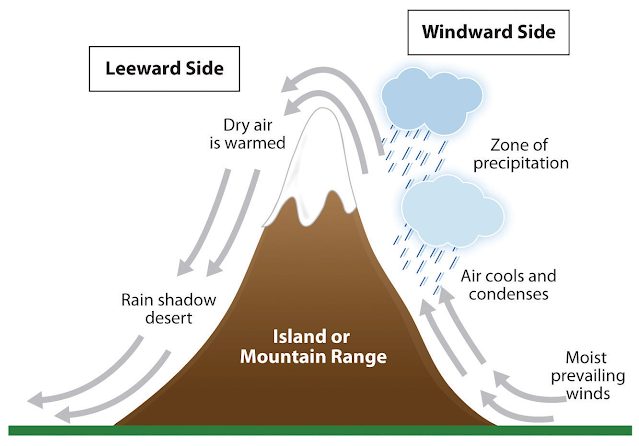
Factors that Affect Precipitation
Precipitation is influenced by a mix of natural elements. Geography plays a critical role. Mountains can trap moist air, leading to heavier rainfall on one side while causing dryness on the other.
Temperature also dictates how precipitation forms. Warmer air holds more moisture, increasing chances for rain or snow as it cools and condenses.
Wind patterns are essential too. They transport humid air from oceans inland, affecting regions far from water sources.
Seasonal changes bring shifts in weather systems as well. Certain months may experience more storms due to atmospheric conditions that favor precipitation.
Humidity levels directly impact cloud formation and the amount of precipitation produced. High humidity often results in significant downpours, whereas lower humidity can lead to light rains or even droughts in some areas.
Understanding these factors helps us appreciate the complex nature of snowfall and rain across our world.
Fun Facts about Precipitation
Precipitation is more than just rain and snow. Did you know that the largest recorded raindrop was 8.0 mm wide? That’s about the size of a marble!
Speaking of sizes, some snowflakes can be as large as dinner plates under perfect conditions. Each one has its own unique design, making them nature's tiny masterpieces.
Have you heard of "frost flowers"? These delicate formations occur when moisture rises from the ground in freezing temperatures, creating intricate ice structures.
In certain regions, particularly during monsoon seasons, rainfall can reach staggering amounts over 467 inches in Matsuyama, India! This makes it one of the wettest places on Earth.
And let’s not forget about “ballooning” spiders. They use strands of silk to catch air currents and travel long distances when it rains or snows. Nature truly finds remarkable ways to adapt!
The Role of Precipitation in the Water Cycle
Precipitation is a vital component of the water cycle. It serves as nature's way of recycling water from the atmosphere back to the Earth's surface. When clouds gather moisture, they inevitably release it in various forms rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Once precipitation falls, it nourishes plants and replenishes rivers and lakes. This process ensures that ecosystems thrive and sustain diverse life forms.
After reaching the ground, some of this water infiltrates into the soil while others flow into larger bodies of water. Through evaporation and transpiration, moisture returns to the sky once more.
This continuous loop maintains balance within our environment and supports agriculture too. Without precipitation playing its role effectively, many regions would face droughts or flooding crises that disrupt daily life considerably.
Unusual Forms of Precipitation
When we think of precipitation, rain and snow usually come to mind. However, nature has some quirky surprises up its sleeve. One fascinating form is sleet, which consists of small ice pellets that bounce off surfaces rather than collecting.
Then there's freezing rain. It starts as liquid droplets but freezes upon contact with cold surfaces, creating a hazardous layer of ice. This phenomenon can transform ordinary landscapes into treacherous terrains.
Another unusual type is graupel. Often confused with hail, this soft pellet forms when supercooled water droplets cling to snowflakes, resulting in light and fluffy balls.
Consider the rare occurrence of fish rain or animal precipitation events where small fish or frogs fall from the sky during strong storms due to waterspouts or tornadoes lifting them high before releasing them back down. Nature never ceases to amaze.
Predicting and Measuring Precipitation
Predicting and measuring precipitation is a blend of science and technology. Meteorologists rely on advanced tools to forecast rain, snow, and other forms of moisture.
Radar systems play a crucial role. They send out signals that bounce off raindrops or snowflakes, helping experts gauge the intensity and movement of precipitation. This data allows for real time forecasts.
Satellites add another layer. High above the Earth, they capture images that reveal cloud patterns and weather systems in motion. These satellites help scientists track storms before they reach populated areas.
Ground-based stations also contribute valuable information. They measure rainfall directly with rain gauges while automated sensors monitor snowfall amounts.
The challenge lies in accuracy. Weather is inherently unpredictable but advances in technology continue to improve our understanding of atmospheric conditions, making it possible to prepare for whatever falls from the sky next.
Impact of Climate Change on Precipitation Patterns
Climate change is reshaping precipitation patterns across the globe. As temperatures rise, moisture in the atmosphere increases, leading to more intense rainfall events.
Some regions experience heavier downpours and flooding, while others face prolonged droughts. This imbalance disrupts ecosystems and agriculture alike.
Snowfall is also affected. Warmer winters mean less snow accumulation in many areas. When it does fall, it's often short-lived due to rising temperatures.
The shift in precipitation can strain water resources. Communities that rely on consistent snowfall for their water supply may find themselves at risk during dry spells.
Additionally, these changes influence weather systems worldwide. Storm tracks alter as warmer air interacts with cooler fronts, creating unpredictable weather outcomes.
Understanding these dynamics helps us adapt to a rapidly changing world where every drop counts.
Conclusion
Precipitation is a fascinating aspect of our world that shapes ecosystems and influences daily life. From the gentle drizzle of rain to the magical transformation into snowflakes, each form plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within nature. Understanding its various types and how they are affected by environmental factors enhances our appreciation for this natural phenomenon.
As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the impact on precipitation is becoming more profound. We can expect shifts in where and how much rain or snow falls, which may lead to both droughts and floods in different regions around the globe.
By exploring precipitation's intricacies from its role in the water cycle to unusual forms like sleet or freezing rain we uncover layers of complexity that underscore its importance. As we adapt our approaches to monitoring and predicting these changes, we become better equipped to handle their implications.
The world of precipitation is vast and varied, inviting us all to observe closely as it unfolds in front of us day by day. Embracing this intricate interplay not only enriches our understanding but also informs how we interact with our environment moving forward.




Comments